Could Irritable Bowel Syndrome Be Causing Women's Constant Stomach Pain?
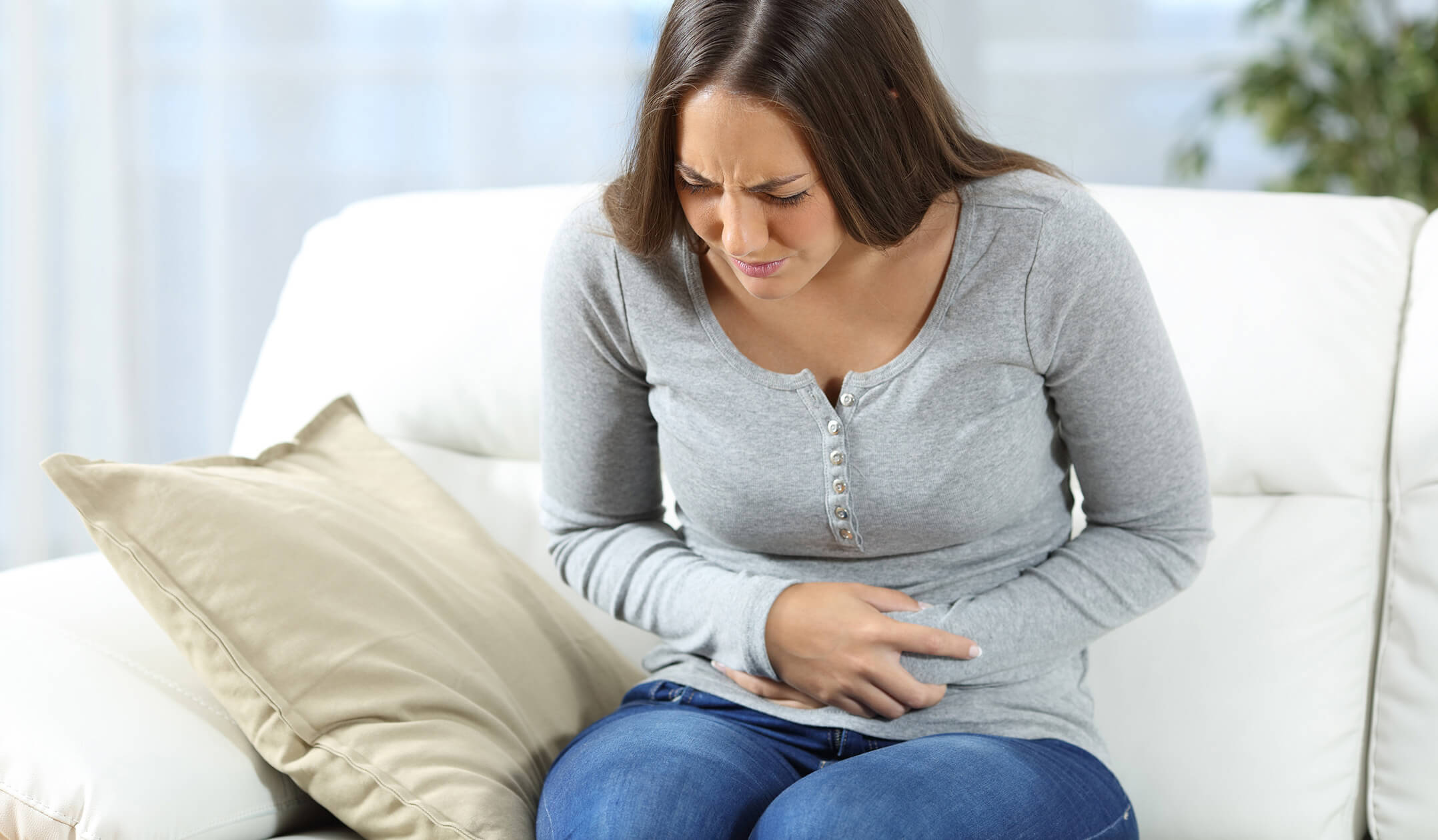
Chronic stomach pain in women can be distressing and challenging to diagnose. One potential culprit that often goes undiagnosed is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). This common gastrointestinal disorder can significantly impact a woman's quality of life. Let's explore whether IBS could be the underlying cause of persistent stomach pain in women.
Understanding Irritable Bowel Syndrome
IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms, primarily abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits, without any detectable organic cause. It affects the large intestine and is a chronic condition that requires long-term management.
Symptoms of IBS
The symptoms of IBS can vary widely but often include:
- Abdominal Pain and Cramping: This is usually relieved or partially relieved by passing a bowel movement.
- Bloating and Gas: Excessive gas and a feeling of fullness are common.
- Diarrhea or Constipation: Some individuals experience diarrhea (IBS-D), others constipation (IBS-C), and some alternate between the two (IBS-M).
- Mucus in the Stool: Presence of white or clear mucus in stool is a symptom of IBS.
Why Women Are More Affected
Studies suggest that IBS is more prevalent in women than men, with women being up to twice as likely to be diagnosed. The reasons for this disparity are not fully understood but may involve hormonal differences, stress responses, and variations in gut sensitivity and motility.
Hormonal Influences
Fluctuations in female hormones, particularly during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause, can exacerbate IBS symptoms. Many women report that their symptoms worsen during menstruation.
Stress and IBS
Stress and anxiety can trigger or worsen IBS symptoms. Women, who statistically report higher levels of stress and anxiety than men, might therefore be more susceptible to IBS.
Diagnosing IBS
Diagnosing IBS typically involves:
- Medical History and Symptom Review: Detailed discussion about symptoms and their patterns.
- Physical Examination: Including abdominal palpation.
- Diagnostic Tests: To rule out other conditions such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and infections. These may include blood tests, stool tests, and endoscopic procedures.
Treatment and Management
There is no cure for IBS, but various treatments can help manage symptoms:
- Dietary Changes: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods (such as FODMAPs), eating smaller, more frequent meals, and ensuring adequate fiber intake can be beneficial.
- Medications: Depending on symptoms, doctors may prescribe fiber supplements, laxatives, anti-diarrheal medications, antispasmodics, or antidepressants.
- Probiotics: Some studies suggest that probiotics may help alleviate IBS symptoms.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and relaxation exercises can be effective.
- Regular Exercise: Helps improve bowel function and reduce stress.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Women experiencing constant stomach pain should consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause. Persistent pain, especially when accompanied by other symptoms such as weight loss, fever, or blood in stools, warrants prompt medical attention to rule out serious conditions.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a common yet often overlooked cause of chronic stomach pain in women. Understanding the symptoms, triggers, and management strategies is crucial for those affected. If you suspect IBS might be behind your constant stomach pain, seeking medical advice is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Managing IBS involves a combination of dietary changes, medication, stress management, and lifestyle adjustments, which can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.