Antiaromatic hydrocarbon boasts unusual stability
Antiaromatic hydrocarbons are typically characterized by their cyclic structure and a specific number of π-electrons that lead to instability. However, certain antiaromatic compounds exhibit unusual stability under specific conditions. Understanding the factors contributing to this stability is essential for chemists and researchers in organic chemistry and materials science.
Key Factors Contributing to Stability
1. Molecular Distortion
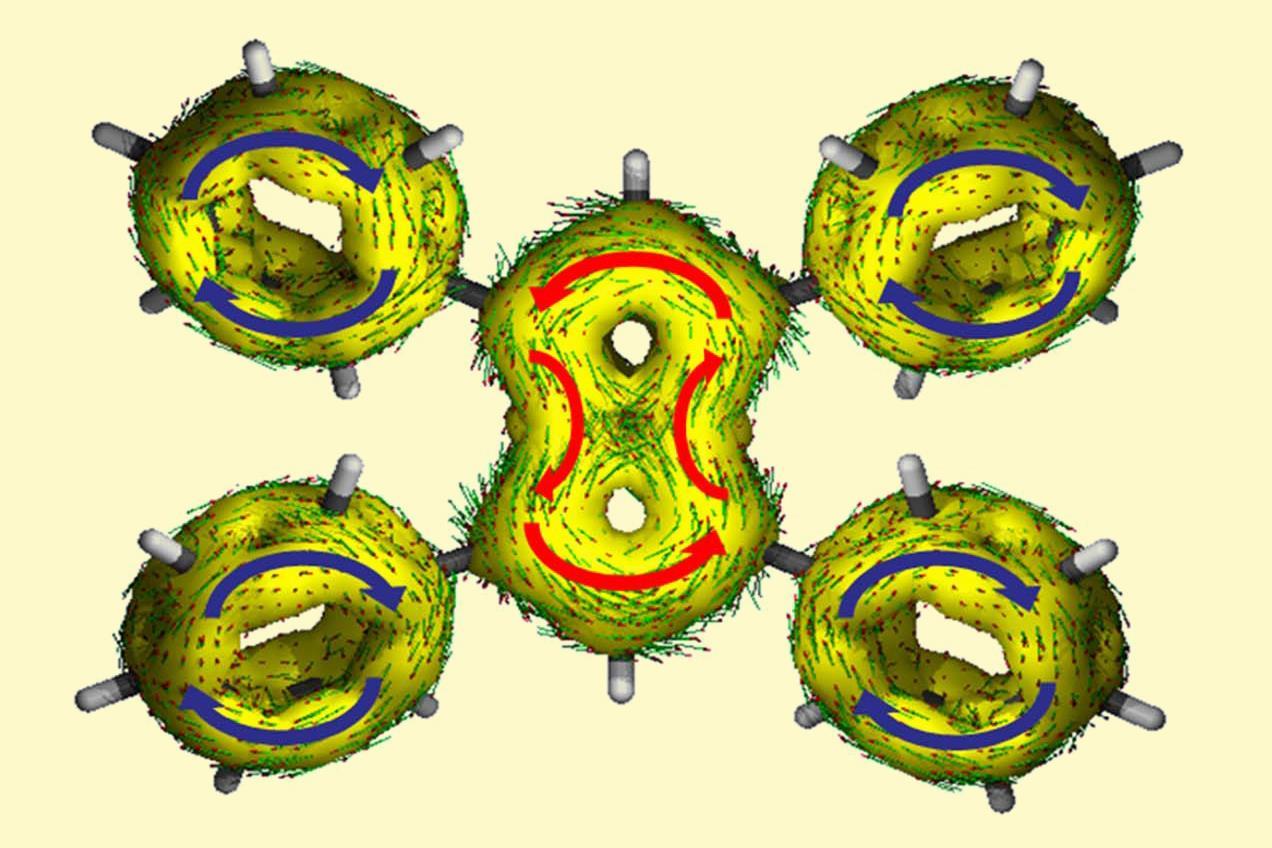
- Non-planarity: Some antiaromatic hydrocarbons can adopt non-planar conformations to relieve the strain associated with their planar structure. For example, cyclooctatetraene, which has 8 π-electrons, prefers a "tub" conformation rather than a flat structure. This distortion helps mitigate the destabilizing effects of antiaromaticity, making the compound more stable than expected.
2. Substituent Effects
- Electron-Withdrawing and Electron-Donating Groups: The presence of substituents can influence the electronic environment of antiaromatic hydrocarbons. Electron-withdrawing groups can stabilize the π-system by reducing electron density, while electron-donating groups can enhance stability by increasing resonance stabilization. The overall effect depends on the specific substituents and their positions on the ring.
3. Hybridization and Resonance
- Increased Hybridization: In some cases, antiaromatic compounds can stabilize through hybridization changes. If the compound can engage in sp² hybridization, it may allow for some degree of resonance stabilization, counteracting the destabilizing effects of antiaromaticity.
4. Formation of Complexes
- Coordination with Metal Ions: Antiaromatic hydrocarbons can form stable complexes with metal ions, which can stabilize the π-electron system. This interaction can lead to decreased reactivity and increased stability, making these compounds more useful in catalysis and materials applications.
5. Environmental Factors
- Solvent Effects: The choice of solvent can significantly impact the stability of antiaromatic compounds. Polar solvents may stabilize charged or polar forms of the compound, while non-polar solvents may not provide the same level of stabilization. Solvation effects can influence the overall energy landscape of the compound.
6. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Stability
- Thermodynamic Stability: Some antiaromatic compounds may be thermodynamically stable under certain conditions, particularly if they can form stable intermediates or products during chemical reactions. Kinetic stability refers to the compound's resistance to undergoing reactions that would lead to its decomposition or transformation.
While antiaromatic hydrocarbons are generally less stable than their aromatic counterparts due to their electronic configuration and structural strain, several factors can enhance their stability. Molecular distortion, substituent effects, hybridization, complex formation, environmental factors, and considerations of thermodynamic and kinetic stability all play crucial roles in determining the viability of these compounds. Understanding these factors is essential for chemists seeking to utilize antiaromatic hydrocarbons in various applications, from organic synthesis to materials science. As research continues, the exploration of stability factors may lead to innovative uses for these unique compounds.