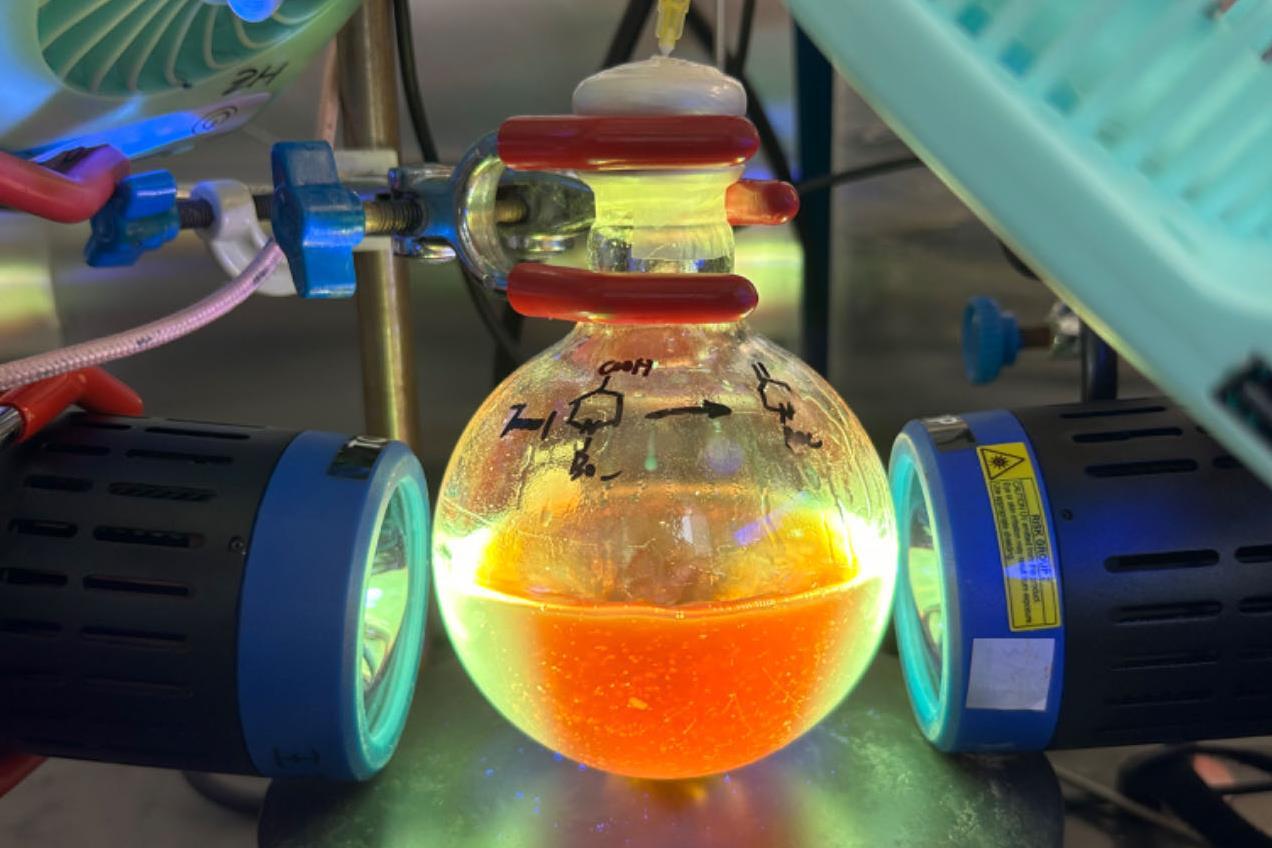
Inducing Cleaner High Temperature Chemistry
High-temperature chemistry plays a vital role in various industrial processes, including energy production, chemical synthesis, and materials processing. However, these processes often come with significant environmental drawbacks, such as greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and waste generation. To mitigate these issues, researchers and industries are exploring innovative approaches to induce cleaner high-temperature chemistry.
1. Advanced Materials and Catalysts
The development of novel materials and catalysts can significantly enhance the efficiency and sustainability of high-temperature chemical reactions. For instance, researchers are investigating the use of:
- Nanostructured materials: These materials exhibit unique properties that can improve reaction rates, selectivity, and stability.
- Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): MOFs can serve as efficient catalysts, allowing for milder reaction conditions and reduced byproduct formation.
- Solid oxide catalysts: These catalysts can facilitate high-temperature reactions with improved selectivity and reduced emissions.
2. Process Intensification and Integration
Process intensification and integration strategies aim to minimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and increase overall efficiency. Some approaches include:
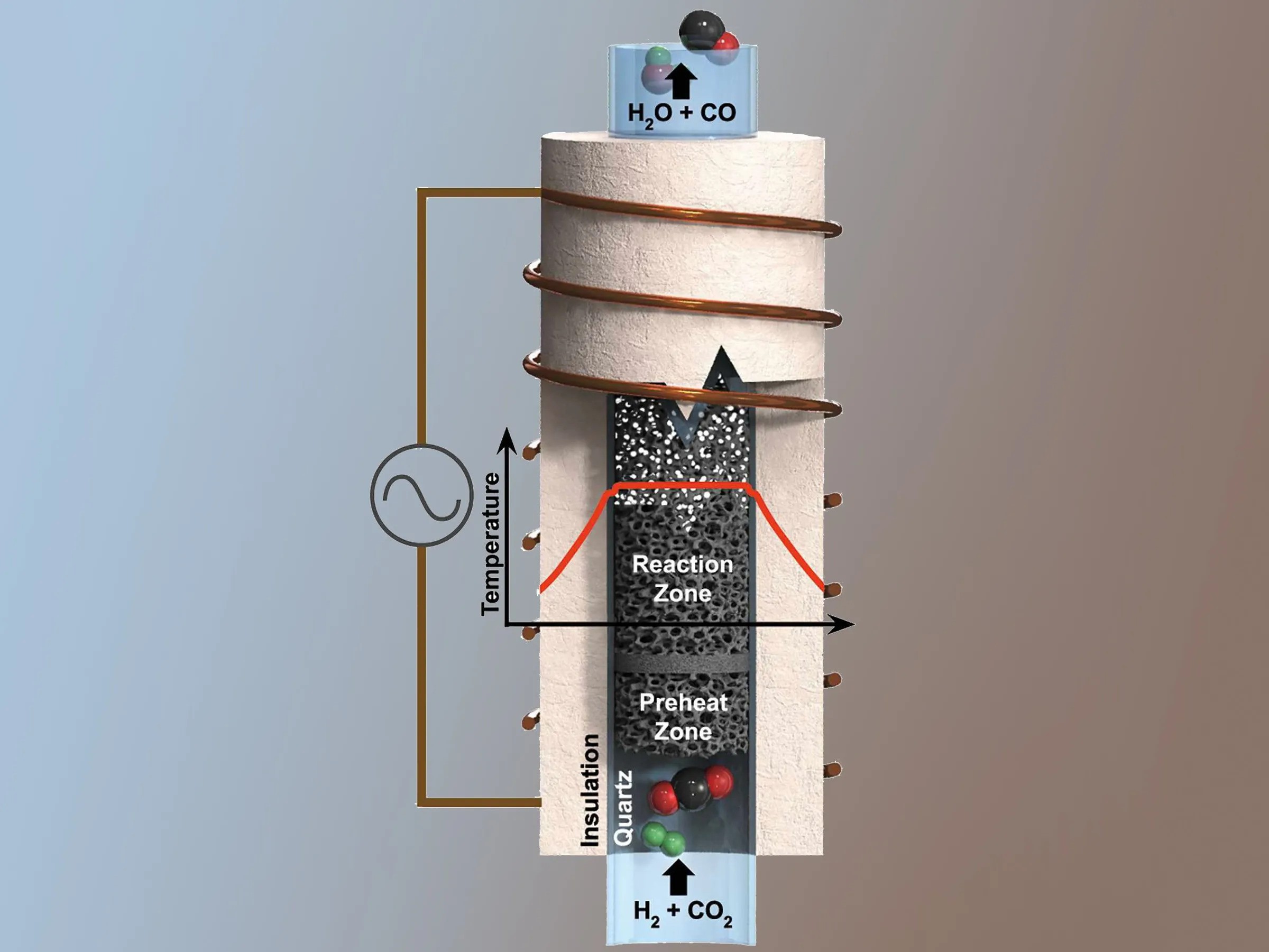
- Microreactor technology: This involves the use of compact, high-surface-area reactors to enhance mass and heat transfer, leading to improved reaction rates and yields.
- Process integration: By combining multiple process steps into a single unit, industries can reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and increase overall efficiency.
3. Alternative Energy Sources and Carriers
Shifting towards alternative energy sources and carriers can significantly reduce the environmental impact of high-temperature chemistry. Some examples include:
- Solar thermal energy: Concentrated solar power can be used to drive high-temperature chemical reactions, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Hydrogen and ammonia as energy carriers: These carriers can facilitate the efficient storage and transportation of energy, enabling the widespread adoption of renewable energy sources.
4. In-Situ Monitoring and Control
Real-time monitoring and control of high-temperature chemical reactions can help optimize process conditions, reduce emissions, and improve product yields. Advanced sensing technologies, such as:
- Optical sensors: These sensors can provide real-time monitoring of reaction conditions, enabling swift adjustments to optimize process performance.
- Machine learning algorithms: By analyzing process data, machine learning algorithms can predict optimal operating conditions, reducing the need for trial-and-error experimentation.
5. Closed-Loop Systems and Recycling
Implementing closed-loop systems and recycling strategies can minimize waste generation and reduce the environmental impact of high-temperature chemistry. This can be achieved through:
- Recycling of catalysts and materials: Closed-loop systems can recover valuable materials and catalysts, reducing the need for virgin resources.
- Waste-to-resource conversion: Industries can convert waste streams into valuable products, such as fuels, chemicals, or materials.